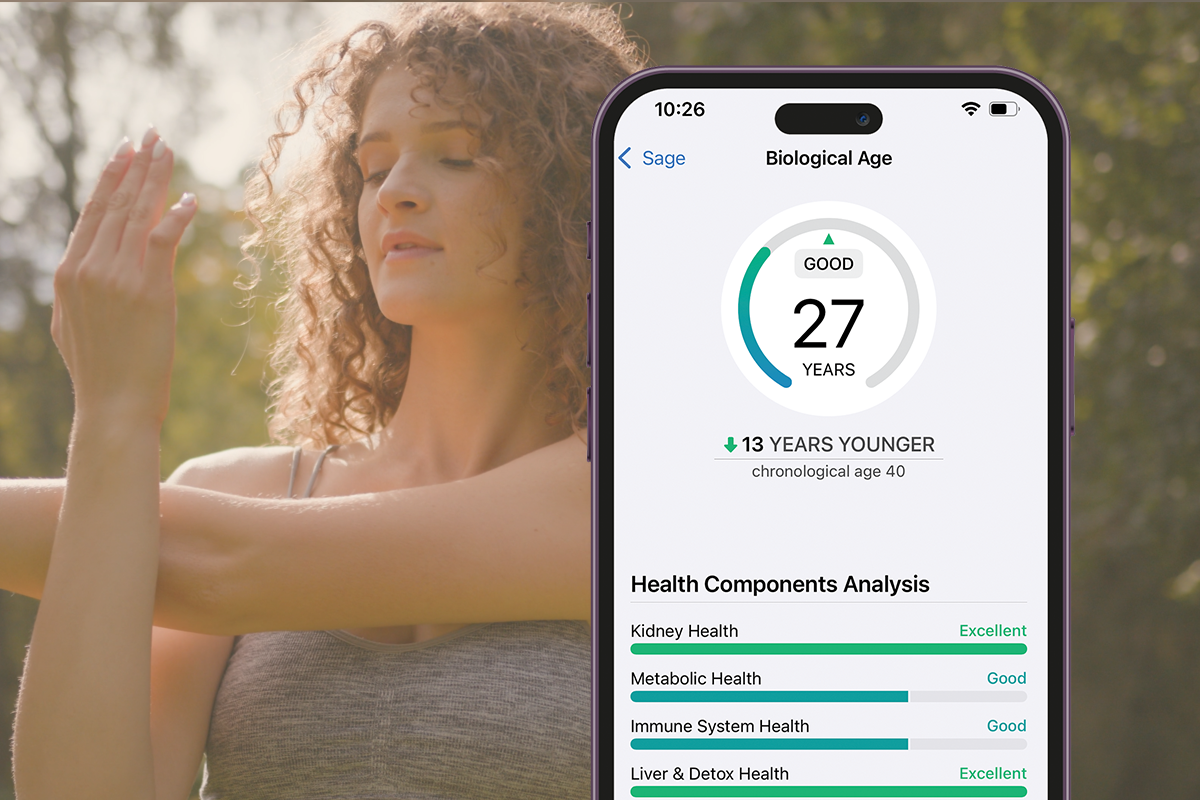
Discover Your True Biological Age
Beyond birthdays: Find out how old your body really is. Your chronological age only tells part of your health story. Your biological age—based on advanced biomarkers in your blood—reveals how quickly you're actually aging at the cellular level.
What is Biological Age?
Biological age measures how well your body is functioning compared to what's typical for your chronological age. It's determined by analyzing specific blood biomarkers that indicate how your critical systems are performing.
This science-backed measurement can be years different from your actual age. Some people are biologically younger than their years (showing slower aging), while others may be biologically older (showing accelerated aging).

Why It Matters
Your biological age is a powerful predictor of:
Overall health and longevity
Disease risk
Cognitive function
Physical performance
More importantly, unlike your chronological age, your biological age can be improved through lifestyle changes, giving you actionable insights to potentially add healthy years to your life.
Simply upload your complete blood test results. Our algorithm will analyze nine key biomarkers to calculate your PhenoAge—a clinically validated biological age measurement developed by leading longevity researchers.
What this tests:
This will give you an accurate view of your Nutrition/Metabolism, Inflammation, Kidney Health, and General Health.
Key Biomarkers:
- Glucose - Fasting
- Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
- Creatinine
- Bun/Creatinine Ratio
- Sodium
- Potassium
- Chloride
What's Included
Biological Age panel will test the following:
Nutrition / Metabolism
- Glucose
- Urea nitrogen
- Creatinine
- Urea nitrogen/Creatinine
- Sodium
- Potassium
- Chloride
- Carbon dioxide
- Calcium
- Protein
- Albumin
- Globulin
- Albumin/Globulin
- Bilirubin
- Alkaline phosphatase
- Glomerular filtration rate/1.73 sq M.predicted
Inflammation
- C reactive protein
Kidney Health
- Creatine kinase
General Health
- Leukocytes
- Erythrocytes
- Hemoglobin
- Hematocrit
- Erythrocyte mean corpuscular volume
- Erythrocyte mean corpuscular hemoglobin
- Erythrocyte mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration
- Erythrocyte distribution width
- Platelets
- Neutrophils/100 leukocytes
- Neutrophils.band form/100 leukocytes
- Neutrophils.band form
- Metamyelocytes/100 leukocytes
- Metamyelocytes
- Myelocytes/100 leukocytes
- Myelocytes
- Promyelocytes/100 leukocytes
- Promyelocytes
- Neutrophils
- Lymphocytes/100 leukocytes
- Lymphocytes.variant/100 leukocytes
- Lymphocytes
- Monocytes/100 leukocytes
- Monocytes
- Eosinophils/100 leukocytes
- Eosinophils
- Basophils/100 leukocytes
- Basophils
- Blasts/100 leukocytes
- Blasts
- Erythrocytes.nucleated/100 leukocytes
- Erythrocytes.nucleated
- Service comment
- Platelet mean volume


